Altered amino acid concentrations in NAFLD: Impact of obesity and insulin resistance - Gaggini - 2018 - Hepatology - Wiley Online Library
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Role of Probiotics in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Does Gut Microbiota Matter?
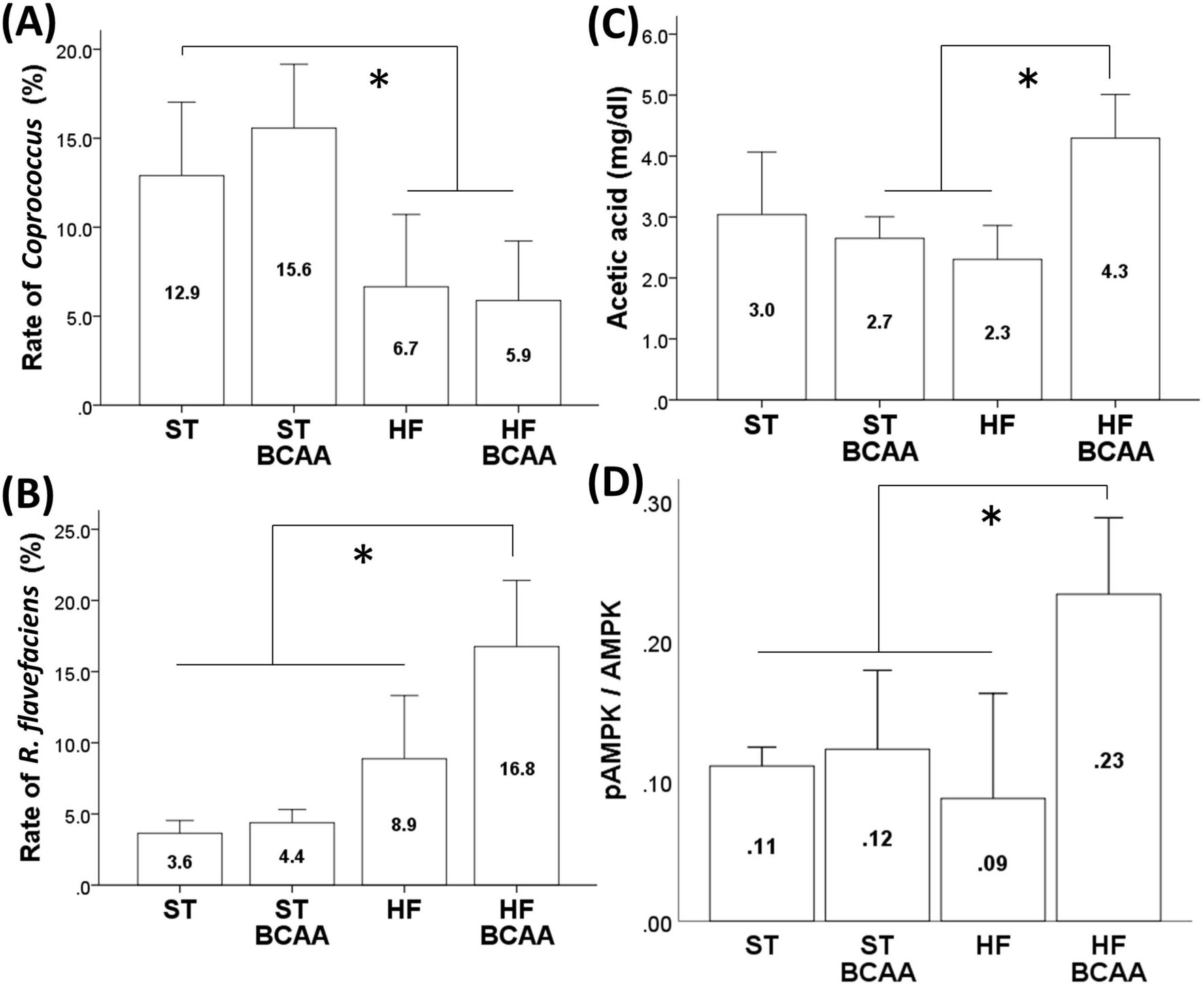
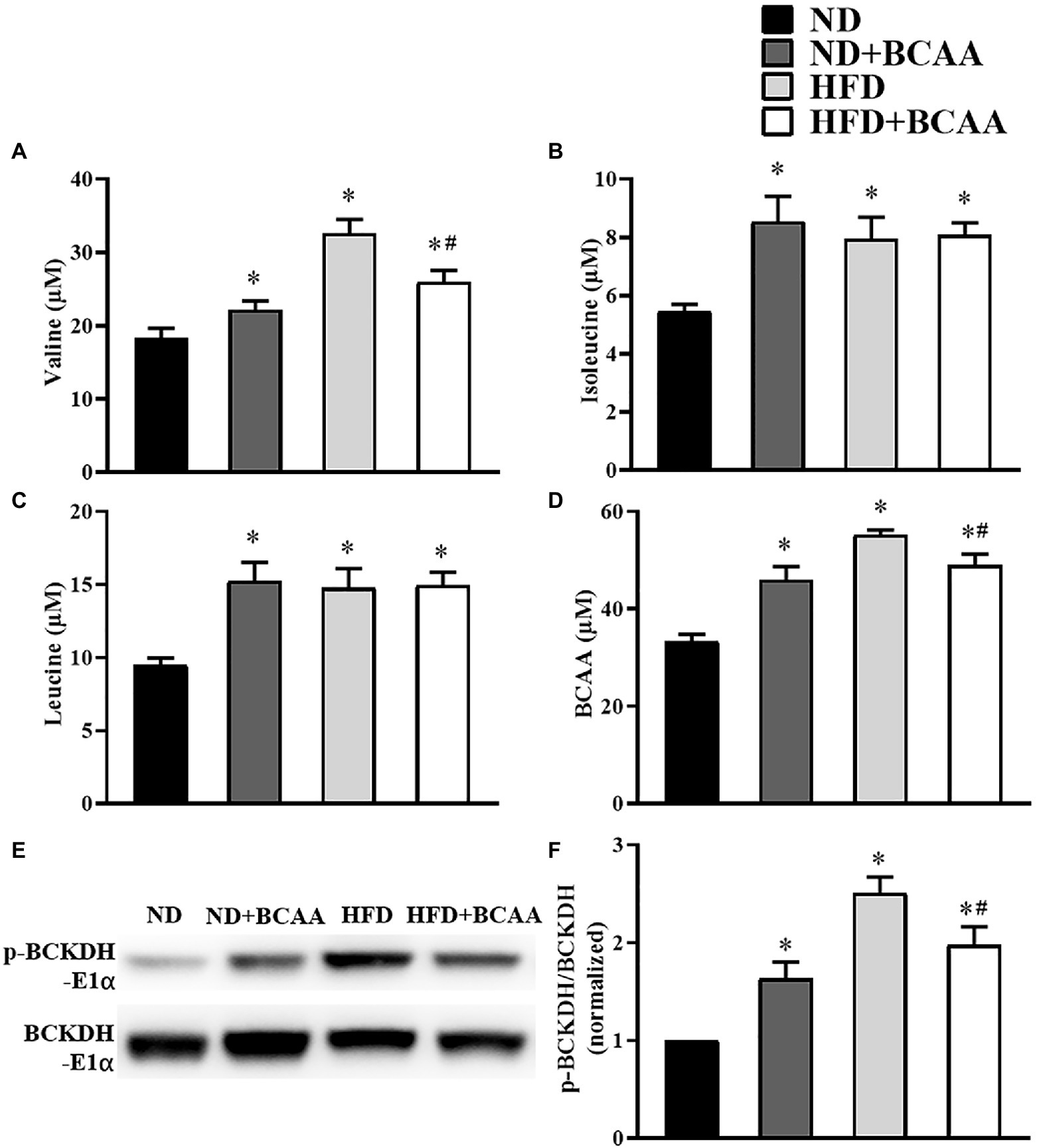
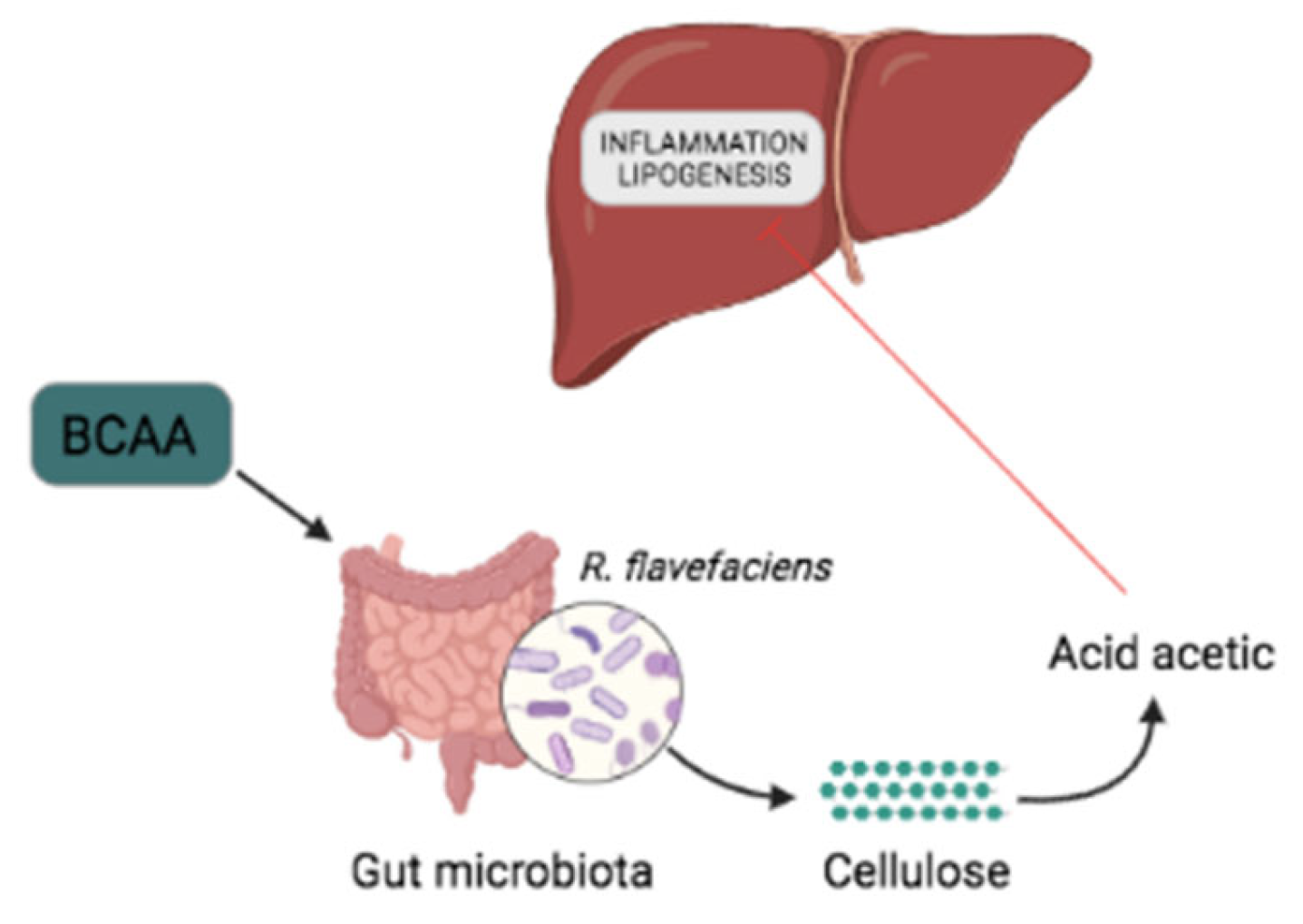
Supplementation of branched-chain amino acids decreases fat accumulation in the liver through intestinal microbiota-mediated production of acetic acid | Scientific Reports

3-Thia fatty acids affect pathways of hepatic BCAA catabolism and 3-HIB... | Download Scientific Diagram
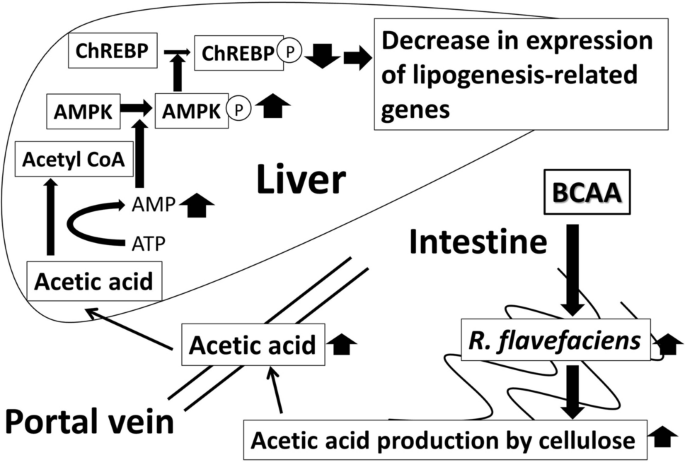
Supplementation of branched-chain amino acids decreases fat accumulation in the liver through intestinal microbiota-mediated production of acetic acid | Scientific Reports
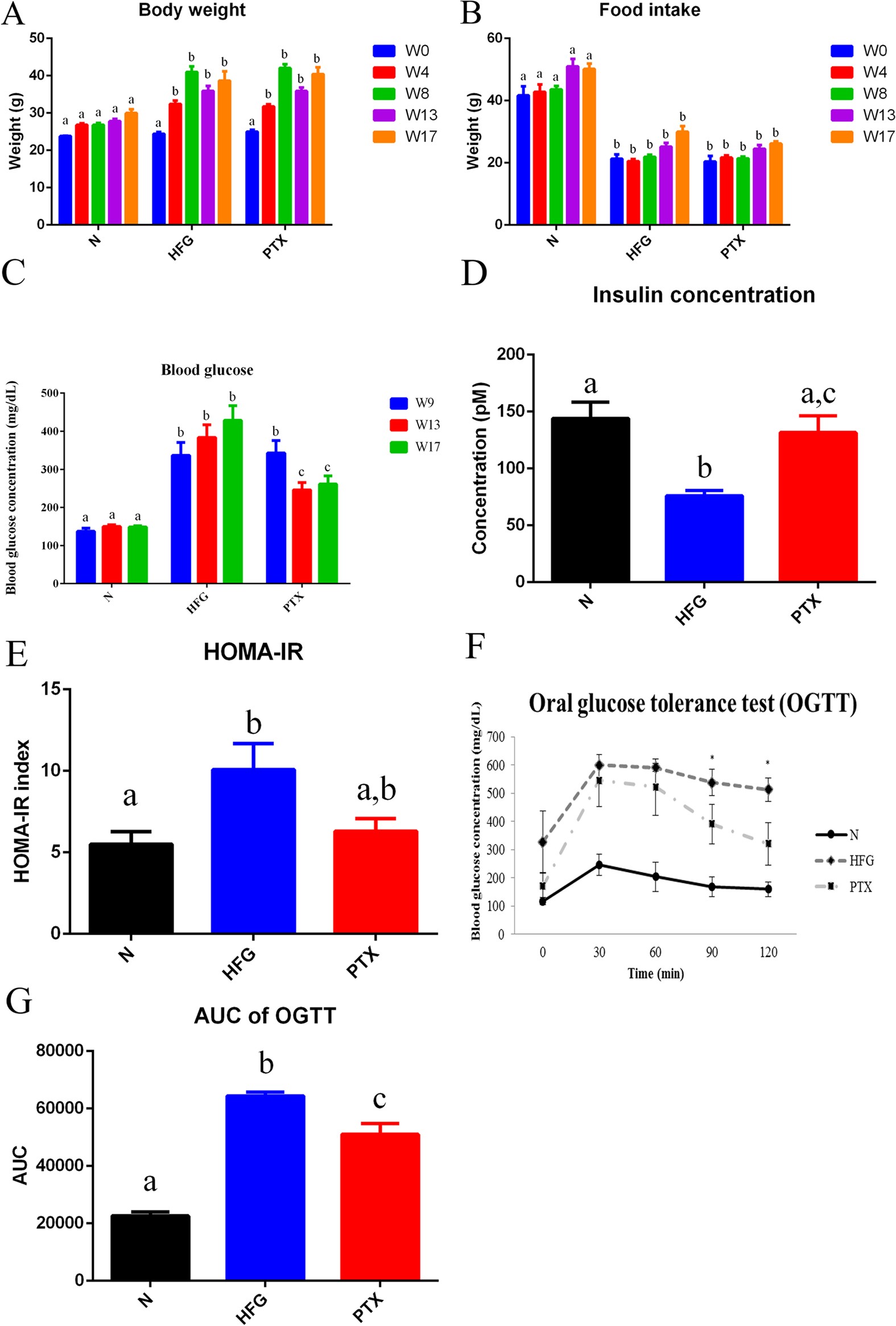
Frontiers | Oral administration of branched-chain amino acids ameliorates high-fat diet-induced metabolic-associated fatty liver disease via gut microbiota-associated mechanisms

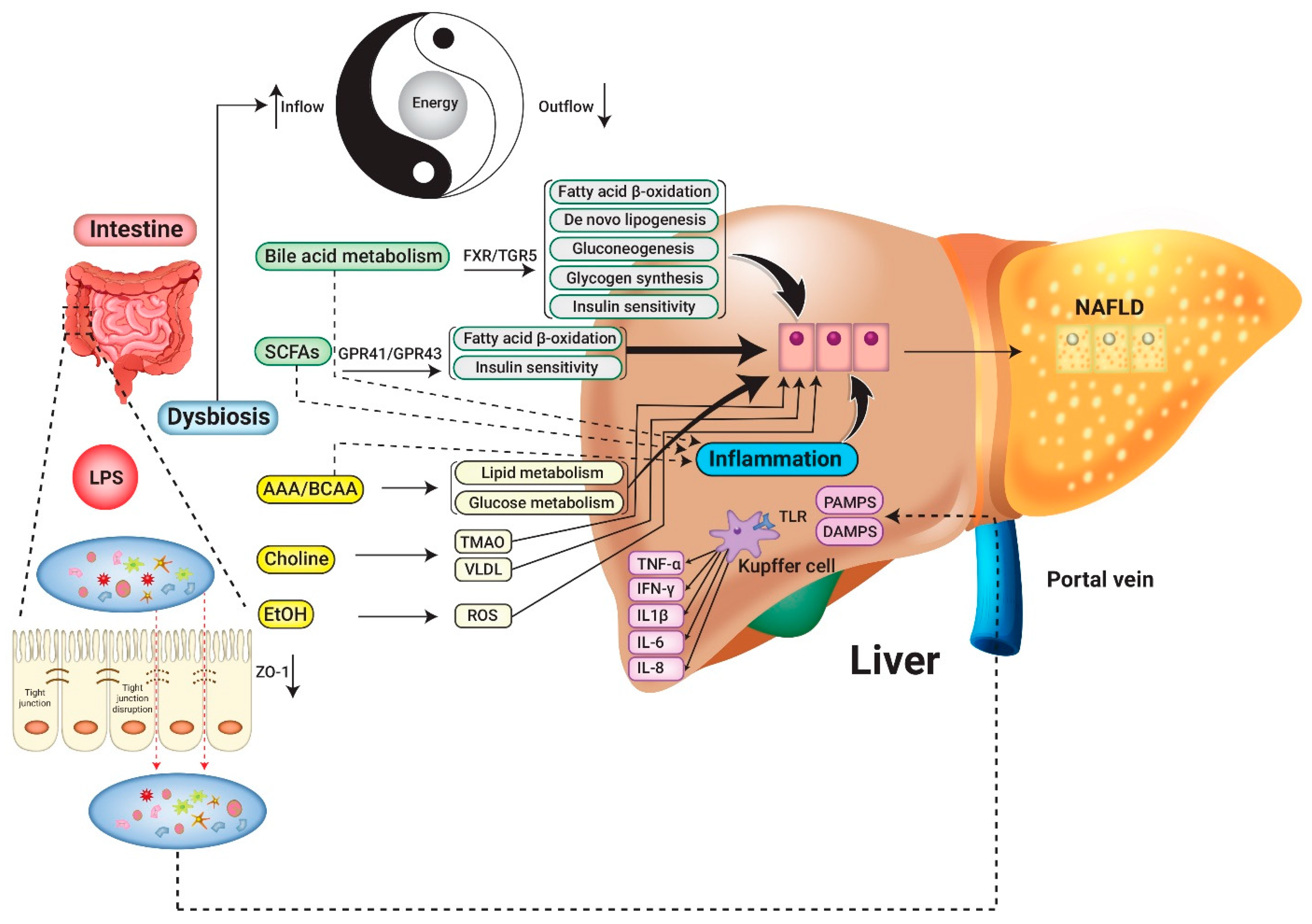
Gut microbiome-targeted therapeutic strategies against nonalcoholic... | Download Scientific Diagram

Muscle-Liver Trafficking of BCAA-Derived Nitrogen Underlies Obesity-Related Glycine Depletion - ScienceDirect
Pentoxifylline ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in hyperglycaemic and dyslipidaemic mice by upregulating fatty acid β-oxidation | Scientific Reports

Branched Chain Amino Acids Cause Liver Injury in Obese/Diabetic Mice by Promoting Adipocyte Lipolysis and Inhibiting Hepatic Autophagy - ScienceDirect

JCI - Mitochondrial role in the neonatal predisposition to developing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease

Branched Chain Amino Acids Cause Liver Injury in Obese/Diabetic Mice by Promoting Adipocyte Lipolysis and Inhibiting Hepatic Autophagy - ScienceDirect
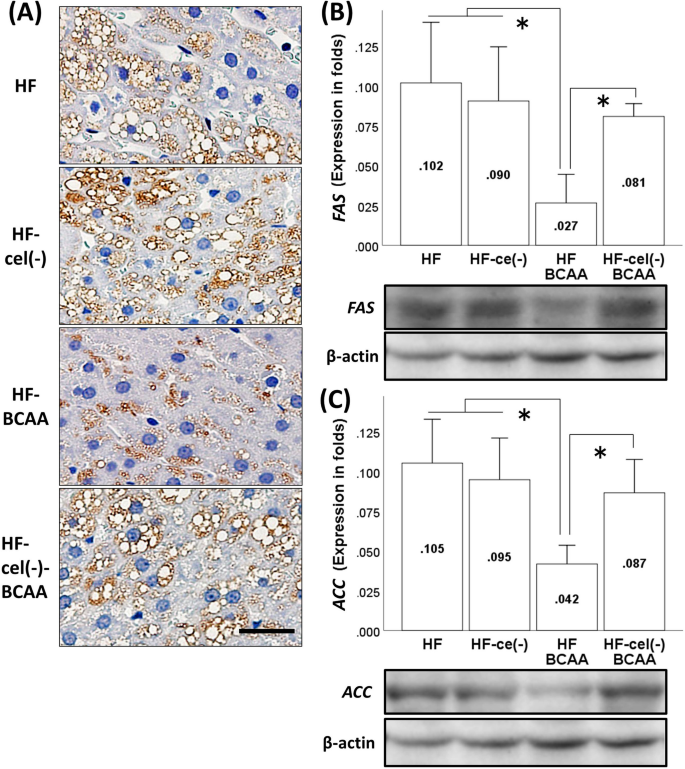
Supplementation of branched-chain amino acids decreases fat accumulation in the liver through intestinal microbiota-mediated production of acetic acid | Scientific Reports

Relationship of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction | JACC: Basic to Translational Science
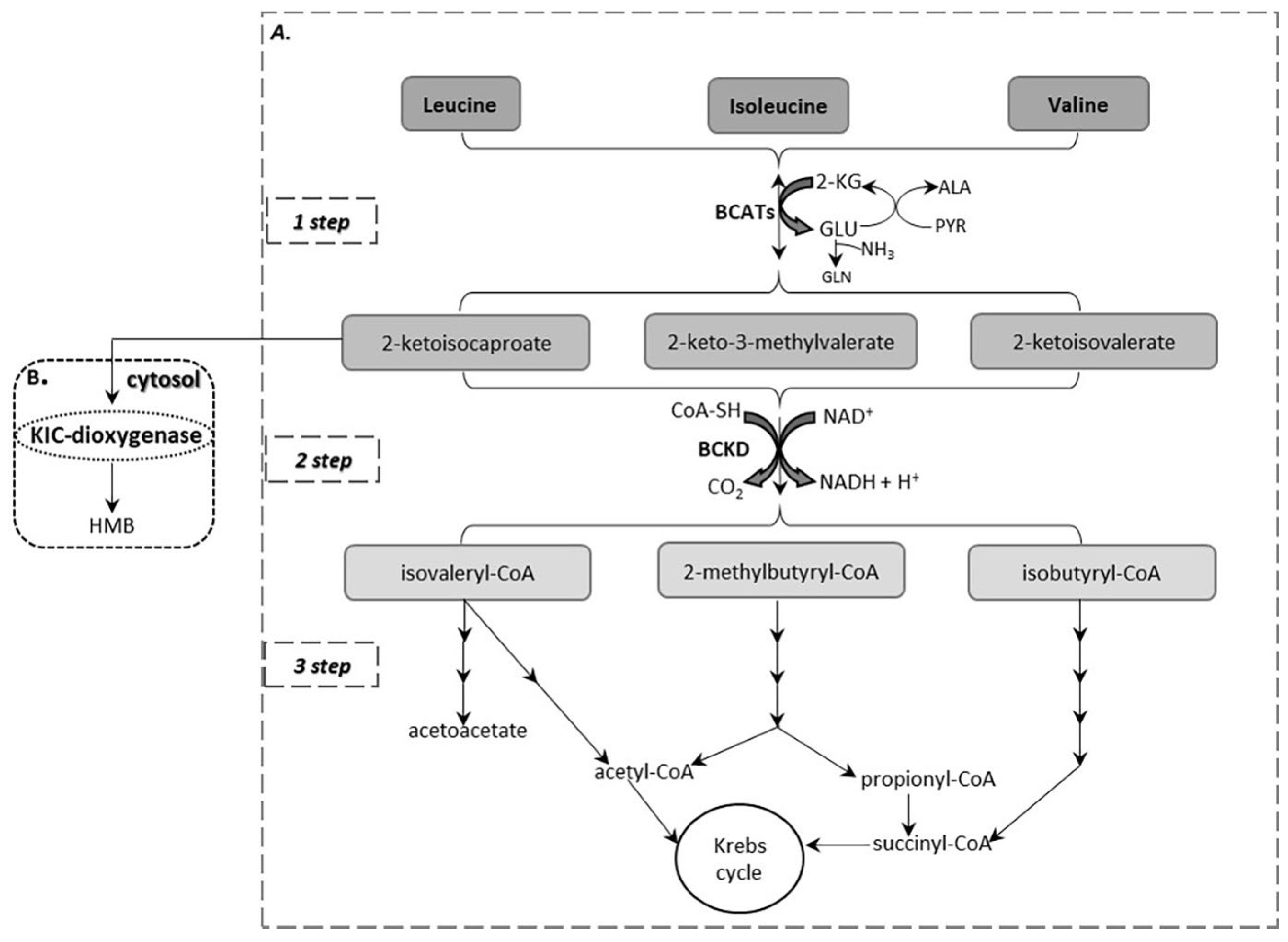
IJMS | Free Full-Text | The Critical Role of the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) Catabolism-Regulating Enzymes, Branched-Chain Aminotransferase (BCAT) and Branched-Chain α-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase (BCKD), in Human Pathophysiology
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity, Cardiovascular Disease and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease